
Some processes will already have “master samples” established for the high and low end of the expected measurement specification. To perform a study, you should first obtain a sample and establish the reference value compared to a traceable standard. More detailed definitions can be found below. Attribute data is classified into specific values where variable or continuous data can have an infinite number of values. The data could be attribute data or variable data. Prior to analyzing the data and or the gages, tools or fixtures we must determine the type of data being collected.
The process, the tools being used (gages, fixtures, instruments, etc.) and the operators are evaluated for proper definition, accuracy, precision, repeatability and reproducibility.
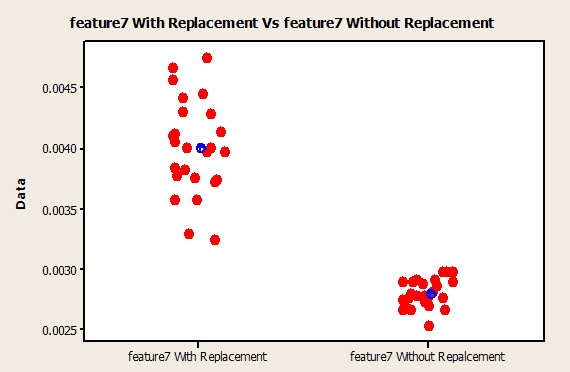
Each tool should have the correct level of discrimination and resolution to obtain useful data. Data collected should be evaluated for bias, stability and linearity.ĭuring an MSA activity, the amount of measurement uncertainty must be evaluated for each type of gage or measurement tool defined within the process Control Plans. We need to evaluate the quality of the data being collected in regards to location and width variation. Our goal is to quantify the effectiveness of the measurement system, analyze the variation in the data and determine its likely source. We should review the measurement data being collected, the methods and tools used to collect and record the data. MSA is a collection of experiments and analysis performed to evaluate a measurement system’s capability, performance and amount of uncertainty regarding the values measured.
TYPE 1 GAGE STUDY MINITAB HOW TO
How to Perform Measurement System Analysis (MSA) MSA could have prevented the problem and assured that accurate useful data was being collected. An ineffective measurement system can allow bad parts to be accepted and good parts to be rejected, resulting in dissatisfied customers and excessive scrap. The problem was that the gage did not have adequate resolution to detect the non-conforming parts. The operator was following the inspection plan and using the assigned gages for the inspection. The process was audited and found that the parts were being produced out of spec. The parts were not properly snapping together to form an even surface or would not lock in place. A major manufacturing company began receiving calls from several of their customers reporting non-compliant materials received at their facilities sites. Good reliable data can prevent wasted time, labor and scrap in a manufacturing process. Why Perform Measurement System Analysis (MSA)Īn effective MSA process can help assure that the data being collected is accurate and the system of collecting the data is appropriate to the process. The sum of these two values represents the total variation in a measurement system. Most MSA activities examine two primary sources of variation, the parts and the measurement of those parts.
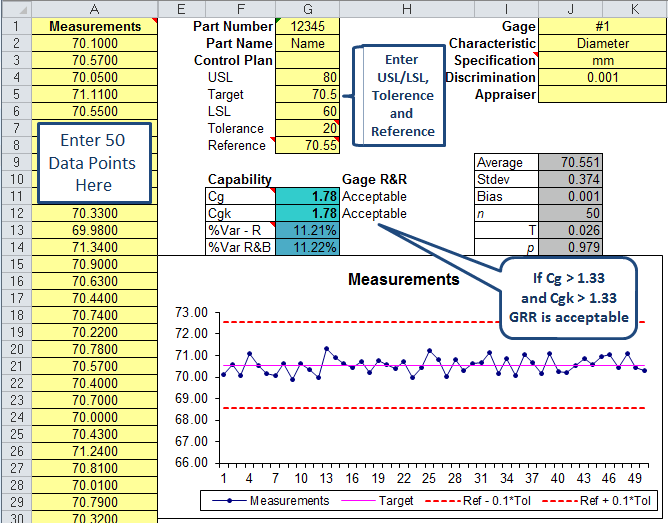
Evaluation of a measurement system should include the use of specific quality tools to identify the most likely source of variation. Environmental factors – temperature, humidity, etc.Īll of these possible sources of variation should be considered during Measurement System Analysis.
Items to be measured – the part or material samples measured, the sampling plan, etc.Tools / Equipment – gages, fixtures, test equipment used and their associated calibration systems.Personnel – the operators, their skill level, training, etc.The sources of variation in a measurement process can include the following:
TYPE 1 GAGE STUDY MINITAB SOFTWARE
It can also include a collection of gages, fixtures, software and personnel required to validate a particular unit of measure or make an assessment of the feature or characteristic being measured. A measurement system has been described as a system of related measures that enables the quantification of particular characteristics. What is a Measurement System?īefore we dive further into MSA, we should review the definition of a measurement system and some of the common sources of variation. MSA is used to certify the measurement system for use by evaluating the system’s accuracy, precision and stability. Variation in the measurement process can directly contribute to our overall process variability. MSA is defined as an experimental and mathematical method of determining the amount of variation that exists within a measurement process. What is Measurement System Analysis (MSA)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
